Russian Scientists Have Studied Marine Worm with Unique Spermatozoa
Russian scientists at A.V. Zhirmunsky National Scientific Centre of Marine Biology, HSE University, and Moscow State University have studied Phoronis embryolabi, a rare species of marine invertebrate found in the waters of the Sea of Japan. This species is notable for its unique reproductive system, which includes the development of larvae within the parent’s body and an unusual sperm structure. The study's findings contribute to our understanding of the evolutionary adaptations of marine organisms to extreme conditions. The study has been published in Zoologischer Anzeiger.
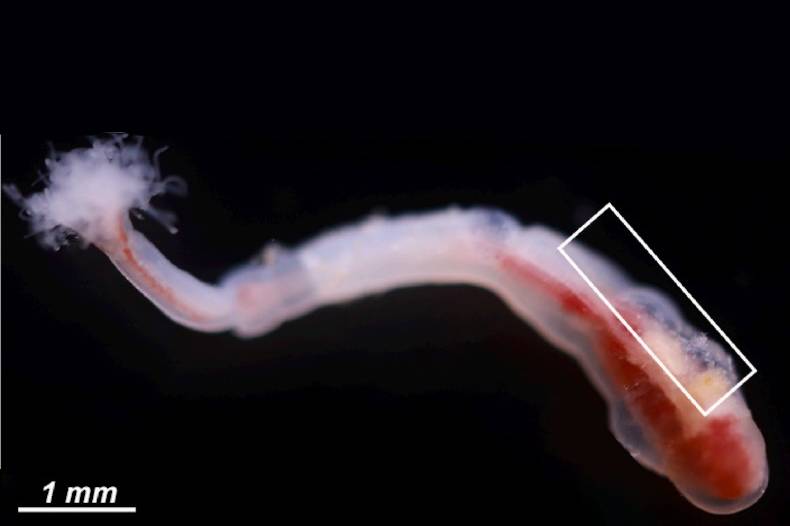
Phoronis embryolabi is a small marine worm that is viviparous, meaning it gives birth to live young, with larvae developing inside the parent’s body. This is an important adaptation for Phoronis embryolabi, which lives as a commensal organism—a type of symbiotic relationship where the commensal benefits while the host remains unaffected—in the holes of burrowing shrimp. It has been discovered that the reproductive process in this species involves the formation of spermatozoa with an unusual structure.
Spermatozoa are filamentous cells capable of moving within the confined spaces of the body. They develop in vasoperitoneal tissue (VPT) that surrounds blood vessels. 'This structure enables spermatozoa to move efficiently through narrow spaces filled with cells and embryos,' according to Elena Temereva, Professor of the Joint Department with RAS Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology.
Unlike other phoronid species, whose spermatozoa are V-shaped, Phoronis embryolabi’s spermatozoa maintain an elongated shape throughout all stages of maturity. The flagellum, essential for movement, is closely aligned with the cell body, which aids in movement through the narrow spaces of the body cavity. This is important, because the numerous embryos and other cells developing inside the body create additional challenges for sperm movement.
Sperm cells in Phoronis embryolabi, known as introsperm, possess unique adaptations typical of species with internal fertilisation. To reach the eggs, they must navigate through dense layers of cells and squeeze in the narrow spaces within the body. The researchers found that these spermatozoa are equipped with a collar around the base of the flagellum, which, along with undulating movements, enables them to move through the densely packed inner spaces of the animal. This movement resembles that of certain single-cell parasites, such as trypanosomes, which use similar mechanisms to move through a viscous medium.
For comparison, in other phoronid species, such as Phoronis pallida and Phoronopsis harmeri, introsperm are V-shaped cells composed of two parts: one part is the flagellum, while the other contains the nucleus and mitochondria. In Phoronis embryolabi, all components of the sperm are closely interconnected, which enhances their ability to move efficiently through narrow spaces. In addition, their spermatozoa are shorter than those of other species, which may also be an adaptation to the habitat conditions.
The study of spermatogenesis and sperm structure in Phoronis embryolabi provides valuable insights into how organisms adapt to extreme conditions. This information helps deepen our understanding of the evolution of reproductive biology in marine invertebrates and the factors that have influenced the development of complex reproductive strategies.
The unique adaptations of spermatozoa in Phoronis embryolabi are a crucial component of this species' survival strategy. The ability to move through narrow spaces and fertilise eggs in a body filled with embryos and other cells is an example of a successful evolutionary adaptation.
The research was carried out with support from the Russian Science Foundation.
See also:
Scientists Discover Link Between Brain's Structural Features and Autistic Traits in Children
Scientists have discovered significant structural differences in the brain's pathways, tracts, and thalamus between children with autism and their neurotypical peers, despite finding no functional differences. The most significant alterations were found in the pathways connecting the thalamus—the brain's sensory information processing centre—to the temporal lobe. Moreover, the severity of these alterations positively correlated with the intensity of the child's autistic traits. The study findings have been published in Behavioural Brain Research.
Earnings Inequality Declining in Russia
Earnings inequality in Russia has nearly halved over the past 25 years. The primary factors driving this trend are rising minimum wages, regional economic convergence, and shifts in the returns on education. Since 2019, a new phase of this process has been observed, with inequality continuing to decline but driven by entirely different mechanisms. These are the findings made by Anna Lukyanova, Assistant Professor at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, in her new study. The results have been published in the Journal of the New Economic Association.
HSE Scientists Develop Application for Diagnosing Aphasia
Specialists at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed an application for diagnosing language disorders (aphasia), which can result from head injuries, strokes, or other neurological conditions. AutoRAT is the first standardised digital tool in Russia for assessing the presence and severity of language disorders. The application is available on RuStore and can be used on mobile and tablet devices running the Android operating system.
HSE Researchers Discover Simple and Reliable Way to Understand How People Perceive Taste
A team of scientists from the HSE Centre for Cognition & Decision Making has studied how food flavours affect brain activity, facial muscles, and emotions. Using near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), they demonstrated that pleasant food activates brain areas associated with positive emotions, while neutral food stimulates regions linked to negative emotions and avoidance. This approach offers a simpler way to predict the market success of products and study eating disorders. The study was published in the journal Food Quality and Preference.
Russian Scientists Demonstrate How Disorder Contributes to Emergence of Unusual Superconductivity
Researchers at HSE University and MIPT have investigated how the composition of electrons in a superconductor influences the emergence of intertype superconductivity—a unique state in which superconductors display unusual properties. It was previously believed that intertype superconductivity occurs only in materials with minimal impurities. However, the scientists discovered that the region of intertype superconductivity not only persists but can also expand in materials with a high concentration of impurities and defects. In the future, these superconductors could contribute to the development of highly sensitive sensors and detectors. The study has been published in Frontiers of Physics.
HSE Scientists Take Important Step Forward in Development of 6G Communication Technologies
Researchers at HSE MIEM have successfully demonstrated the effective operation of a 6G wireless communication channel at sub-THz frequencies. The device transmits data at 12 Gbps and maintains signal stability by automatically switching when blocked. These metrics comply with international 6G standards. An article published on arXiv, an open-access electronic repository, provides a description of certain elements of the system.
AI vs AI: Scientists Develop Neural Networks to Detect Generated Text Insertions
A research team, including Alexander Shirnin from HSE University, has developed two models designed to detect AI-generated insertions in scientific texts. The AIpom system integrates two types of models: a decoder and an encoder. The Papilusion system is designed to detect modifications through synonyms and summarisation by neural networks, using one type of models: encoders. In the future, these models will assist in verifying the originality and credibility of scientific publications. Articles describing the Papilusion and AIpom systems have been published in the ACL Anthology Digital Archive.
Acoustic Battles for the Harem: How the Calls of Siberian Wapiti Reveal Their Status and Individuality
Researchers at HSE University, Lomonosov Moscow State University, and the A.N. Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution of the Russian Academy of Sciences have studied the distinctive vocalisations of Siberian wapiti (Cervus canadensis sibiricus) stags during the peak of the mating season, when males produce rutting calls (bugles) to attract females (hinds) and deter rivals. The scientists have discovered how the acoustic parameters of these rutting calls reflect the stag's status—whether he currently holds a harem or is still attempting to acquire one—as well as his individual characteristics. The study has been published in Journal of Zoology.
Z-Flipons: How Specific DNA Regions Help Regulate Gene Function
Researchers at HSE University and InsideOutBio have applied machine learning to identify the location and functions of mirror-twisted DNA structures, known as Z-flipons, in human and mouse genomes. The scientists discovered which Z-DNA regions were conserved in both species throughout evolution and demonstrated for the first time that Z-DNA accelerates the process of creating RNA copies of genes. The findings will contribute to the development of new treatments for genetic diseases. The study has been published in Scientific Reports.
HSE Researchers Develop Python Library for Analysing Eye Movements
A research team at HSE University has developed EyeFeatures, a Python library for analysing and modelling eye movement data. This tool is designed to simplify the work of scientists and developers by enabling them to efficiently process complex data and create predictive models.