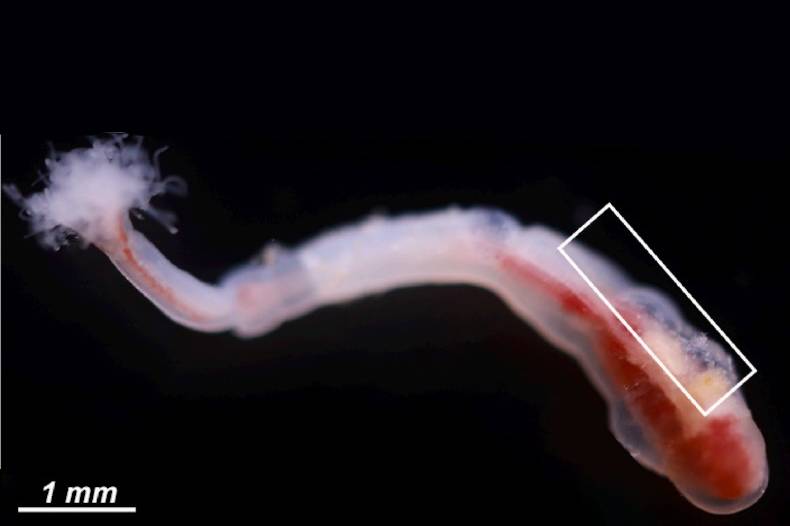
Russian Scientists Have Studied Marine Worm with Unique Spermatozoa
Russian scientists at Zhirmunsky National Scientific Centre of Marine Biology, HSE University, and Moscow State University have studied Phoronis embryolabi, a rare species of marine invertebrate found in the waters of the Sea of Japan. This species is notable for its unique reproductive system, which includes the development of larvae within the parent’s body and an unusual sperm structure. The study's findings contribute to our understanding of the evolutionary adaptations of marine organisms to extreme conditions. The study has been published in Zoologischer Anzeiger.
Biologists at HSE University Warn of Potential Errors in MicroRNA Overexpression Method
Researchers at HSE University and the RAS Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry have discovered that a common method of studying genes, which relies on the overexpression of microRNAs, can produce inaccurate results. This method is widely used in the study of various pathologies, in particular cancers. Errors in experiments can lead to incorrect conclusions, affecting the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. The study findings have been published in BBA.

Researchers Discover Genetic Bridge between Ancient and Modern Populations of North Caucasus
Although the North Caucasus played a crucial role in the ancient colonisation of Eurasia and the shaping of its cultural and genetic heritage, the genetic history of its indigenous cultures has not yet been fully explored. Scientists have, for the first time, conducted deep sequencing of ancient DNA from members of the Koban culture that emerged in the late Bronze Age in the North Caucasus and compared this genetic data with that of modern populations of the Caucasus. Their findings confirm the role of Koban culture carriers as an ancient genetic bridge between the Bronze and Iron Ages in the North Caucasus. The study has been published in the European Journal of Human Genetics.

Early Molecular Diagnosis of Cancer Proven More Cost-Effective Than Subsequent Treatment of Advanced Disease
Applying expensive diagnostic methods in clinical practice will ultimately cost society 5 to 10 times less than the expenditures associated with late-stage cancer treatment, including subsequent disability pensions and sick leave payments—these are the findings from a study conducted by researchers at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences Marina Kolosnitsyna and Anastasia Vladimirskaya in collaboration with colleagues at EVOGEN, a medical genetic laboratory, and the Department of Health of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The study results have been published in Social Aspects of Population Health.

Scientists Discover Cause of Metastasis Formation in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
An international team of researchers including scientists at the HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology has identified factors which can increase the aggressiveness of tumours in patients with colorectal cancer. An isoform of CD44 protein has been found to play a pivotal role in the development of metastases. The study findings have been published in Molecular Oncology.

Scientists Have Developed a Model of Malignant Prostate Tumour and Used It to Test Drug Efficacy
Researchers from HSE University and the Russian Ministry of Health National Medical Research Radiological Centre have successfully generated a three-dimensional laboratory model of prostate cancer and used the model for testing an anti-tumour drug. In the future, this approach has the potential to significantly enhance the efficacy of cancer treatment for patients. The study’s findings have been published in Cancer Urology.

Nanai and Chukchi Found Intolerant to 'Mushroom Sugar'
A team of researchers from HSE University, the RAS Research Centre for Medical Genetics, and the Moscow State University Institute of Anthropology have examined the impact of the human genotype on the production of trehalase, an enzyme responsible for metabolising 'mushroom sugar'. The researchers examined 1,068 DNA samples collected from inhabitants of northern and Arctic regions of Russia and found that the overall risk of trehalase deficiency in certain indigenous northern populations can be as high as 60–70%. The paper has been published in Problems of Nutrition.
Conserved microRNAs and Flipons Shape Gene Expression
An international team, including researchers of the HSE Faculty of Computer Science, has discovered a new mechanism of gene regulation in which microRNA assumes a central role. These non-coding molecules influence the DNA regions within genes that govern embryonic development. The study contributes to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the diverse genetic programs found in complex multicellular organisms. The paper has been published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.

Research Finds Genes Associated with Most Aggressive Kidney Cancer
HSE researchers have found genes characteristic of the most aggressive subtype of clear cell renal carcinoma. Having studied data on tumour samples from 456 patients, Grigory Puzanov, research fellow at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science International Laboratory of Bioinformatics, identified cancer subtypes associated with either a favourable or unfavourable course of the disease. The paper is published in Scientific Reports.

Microfluidic Chip Used to Test Drug Toxicity
A team including HSE researchers has developed a way to use microfluidic chips to assess the toxic effects of drugs on humans. This device will help identify and minimise the side effects of drugs during the preclinical trial stage and reduce the need for animal experiments. The study is published in Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine.